File Storage Quickstart
It is very easy to upload and manage files in AirCode, which can be done through one line of code in aircode.files, and each uploaded file will have a CDN-accelerated access address.
Objectives
- Learn to use
const file = await aircode.files.upload(content, name?)to upload files - Learn to use
const content = await aircode.files.downloadAsBuffer(file)to download files - Learn to use
await aircode.files.delete(file)to delete files
Use upload to Upload Files
A file can be uploaded to AirCode by calling the upload method. In addition, upload can also accept an additional optional name parameter, which can be used to specify the file name.
For example, we upload a plain text file:
const aircode = require('aircode');
module.exports = async function (params, context) {
// Use `aircode.files.upload` to upload a file
const file = await aircode.files.upload(
'Hello World', // The content as string
'hello.txt' // Optional. The name of file
);
return {
file
};
}
const aircode = require('aircode');
module.exports = async function (params, context) {
// Use `aircode.files.upload` to upload a file
const file = await aircode.files.upload(
'Hello World', // The content as string
'hello.txt' // Optional. The name of file
);
return {
file
};
}
Click Debug, then you can see the following results in the Response area:
{
"file": {
"_id": "63a130c830d47f9de61a57f5",
"name": "hello.txt",
"url": "https://umwsep.hk.aircodecdn.com/hello.1671508168232_j93ad0cmqrg.txt",
"type": "text/plain",
"size": 11,
"createdAt": "2022-12-20T03:49:28.375Z",
"updatedAt": "2022-12-20T03:49:28.375Z"
}
}
{
"file": {
"_id": "63a130c830d47f9de61a57f5",
"name": "hello.txt",
"url": "https://umwsep.hk.aircodecdn.com/hello.1671508168232_j93ad0cmqrg.txt",
"type": "text/plain",
"size": 11,
"createdAt": "2022-12-20T03:49:28.375Z",
"updatedAt": "2022-12-20T03:49:28.375Z"
}
}
Indicates that the file is uploaded successfully, and a CDN-accelerated access address is generated. Open the URL directly in your browser to see the file content.
https://umwsep.hk.aircodecdn.com/hello.1671508168232_j93ad0cmqrg.txt
https://umwsep.hk.aircodecdn.com/hello.1671508168232_j93ad0cmqrg.txt
Tips
AirCode will generate a unique identifier to each uploaded file. Even if multiple files with the same name are uploaded, the returned URLs will be independent of each other. There is no need to worry about the same name issue.
View Uploaded Files in Database
Each successfully uploaded file will automatically create a new record in the database's _files table. In the Database area at the bottom of the console, select the _files table to see the file you uploaded.
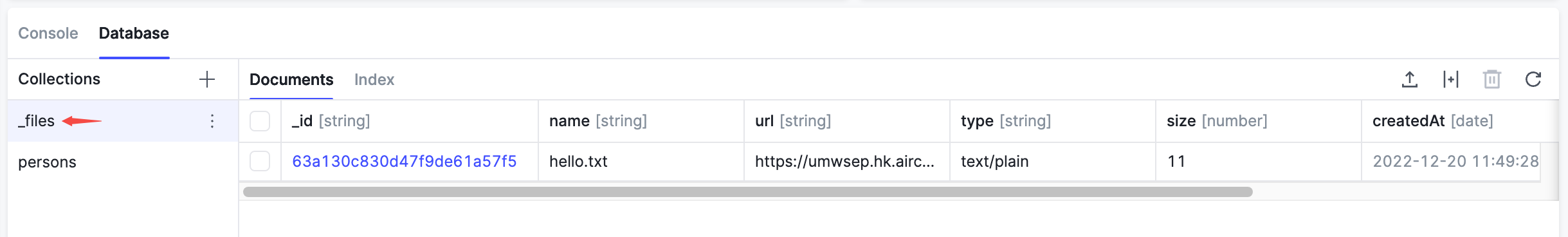
Use download to Download Files
After querying the record in the _files table, call the download API with the record to download the file content to the local for temporary use. By default, the returned result is of type Buffer, which represents the binary information of the file content.
For example, we will find and download the file uploaded in the previous step:
const aircode = require('aircode');
module.exports = async function (params, context) {
// Use `aircode.db.table` to get the `_files` table
const FilesTable = aircode.db.table('_files');
// Use `findOne` to get the file record
const file = await FilesTable.where({ name: 'hello.txt' }).findOne();
// Use `aircode.files.download` to download the file, as Buffer
const content = await aircode.files.download(file);
return {
content,
};
}
const aircode = require('aircode');
module.exports = async function (params, context) {
// Use `aircode.db.table` to get the `_files` table
const FilesTable = aircode.db.table('_files');
// Use `findOne` to get the file record
const file = await FilesTable.where({ name: 'hello.txt' }).findOne();
// Use `aircode.files.download` to download the file, as Buffer
const content = await aircode.files.download(file);
return {
content,
};
}
Click Debug, then you can see the following results in the Response area:
{
"content": {
"type": "Buffer",
"data": [ 72, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 87, 111, 114, 108, 100 ]
}
}
{
"content": {
"type": "Buffer",
"data": [ 72, 101, 108, 108, 111, 32, 87, 111, 114, 108, 100 ]
}
}
Tips
The downloaded file should only be used temporarily for this request, such as text processing, adding watermarks, etc, and you can upload it to the AirCode file storage through upload for persistence after the operation is done.
Use delete to delete files
Calling delete will permanently delete the record from the file storage and the _files table, after which the file is no longer accessible via its URL.
For example, we delete the file uploaded in the previous step.
const aircode = require('aircode');
module.exports = async function (params, context) {
// Use `aircode.db.table` to get the `_files` table
const FilesTable = aircode.db.table('_files');
// Use `findOne` to get the file record
const file = await FilesTable.where({ name: 'hello.txt' }).findOne();
// Use `aircode.files.delete` to delete the file
const result = await aircode.files.delete(file);
return {
result,
};
}
const aircode = require('aircode');
module.exports = async function (params, context) {
// Use `aircode.db.table` to get the `_files` table
const FilesTable = aircode.db.table('_files');
// Use `findOne` to get the file record
const file = await FilesTable.where({ name: 'hello.txt' }).findOne();
// Use `aircode.files.delete` to delete the file
const result = await aircode.files.delete(file);
return {
result,
};
}
Click Debug, then you can see the following results in the Response area:
{
"deletedCount": 1,
"deleted": [
{
"_id": "63637d4807e4d5f7c24b195d",
"url": "https://sample.aircodecdn.com/hello.b10a8db164e07541.txt"
}
]
}
{
"deletedCount": 1,
"deleted": [
{
"_id": "63637d4807e4d5f7c24b195d",
"url": "https://sample.aircodecdn.com/hello.b10a8db164e07541.txt"
}
]
}
Indicates that the file has been successfully deleted. At this point, if you click the refresh button in the Database area, you will see that the record in the _files table has also been deleted.
What's Next?
Congratulations, you have learned the basic of using file storage in AirCode. Wish to know more about the usage of file storage? check out File Storage Overview.